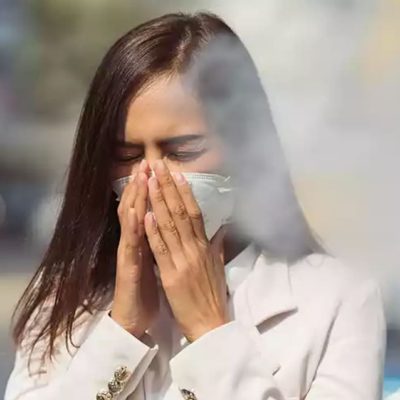
The results of the modelling, published in the journal Environmental Advances, have pinpointed hotspots in the human respiratory system where plastic particles can accumulate, from the nasal cavity and larynx and into the lungs. Dr Saha said evidence was mounting on the significant impact of nano and microplastics on respiratory health and the UTS study would provide … [Read more...]
Women Health News

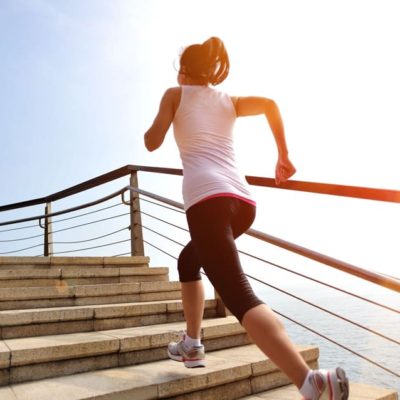
Climb Stairs to Live Longer
Climbing stairs is associated with a longer life, according to research presented today at ESC Preventive Cardiology 2024, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 "If you have the choice of taking the stairs or the lift, go for the stairs as it will help your heart," said study author Dr. Sophie Paddock of the University of East Anglia and … [Read more...]
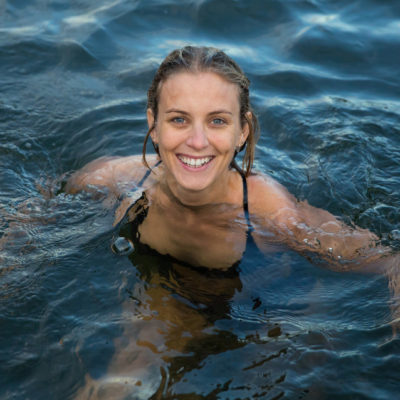
Cold Water Swimming Improves Menopause Symptoms
Menopausal women who regularly swim in cold water report significant improvements to their physical and mental symptoms, finds a new study led by UCL researchers. The research, published in Post Reproductive Health, surveyed 1114 women, 785 of which were going through the menopause, to examine the effects of cold water swimming on their health and wellbeing. The findings … [Read more...]
New Model Predicts How Shoe Properties Affect a Runner’s Performance
A good shoe can make a huge difference for runners, from career marathoners to couch-to-5K first-timers. But every runner is unique, and a shoe that works for one might trip up another. Outside of trying on a rack of different designs, there's no quick and easy way to know which shoe best suits a person's particular running style. MIT engineers are hoping to change that with … [Read more...]
Researchers Discover a New Role for a Protein that helps form Memories
The protein normally performs necessary housekeeping in the brain's hippocampus by working as part of a larger protein complex called the proteasome to destroy other proteins. But researchers in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences' School of Animal Sciences recently noticed this protein, called RPT6, behaving in a previously undetected way. "We found that RPT6 is … [Read more...]
Physical Exercise Boosts Motor Learning and Remembering What one has Learned
Before a violinist tunes their instrument or surgeon stands at the training table to learn the skills needed for a new symphony or surgical procedure, they might consider heading out for a bike ride or run. Once they've practiced the new skill, there's good reason to put on their workout attire again. Indeed, being physically active and elevating one's heart rate has the … [Read more...]
Different Pain Types in Multiple Sclerosis can Cause Difficulty Ataying Active
For patients with multiple sclerosis, a regular exercise routine is important for managing symptoms. Due to different causes of chronic pain though, physical exercise can be more difficult for some. Research published in the Journal of Pain from the University of Michigan found that widespread pain with nociplastic features, also known as WPNF, can make engaging in physical … [Read more...]
Walking More Than Five Flights of Stairs a Day can Cut Risk of Heart Disease by 20 Percent, Study Says
Forget walking 10,000 steps a day. Taking at least 50 steps climbing stairs each day could significantly slash your risk of heart disease, according to a new study from Tulane University. The study, published in Atherosclerosis, found that climbing more than five flights of stairs daily could reduce risk of cardiovascular disease by 20%. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular … [Read more...]
How Sleep Deprivation Can Harm The Brain
Not only does a lack of sleep make you feel awful, research has shown it impairs the brain. What's more, sleep loss over long periods can even increase risk for Alzheimer's and other neurological diseases. Researchers want to understand how sleep deprivation causes this harm. In a new study in ACS' Journal of Proteome Research, a team working with mice has identified a … [Read more...]
Yeast Studies Show That Diet in Early Life Matters for Lifelong Health
Researchers at the Babraham Institute are proposing an alternative link between diet and ageing based on studies in yeast. Dr Jon Houseley and his team have published their experiments, showing that healthy ageing is achievable through dietary change without restriction by potentially optimising diet, and that ill-health is not an inevitable part of the ageing … [Read more...]
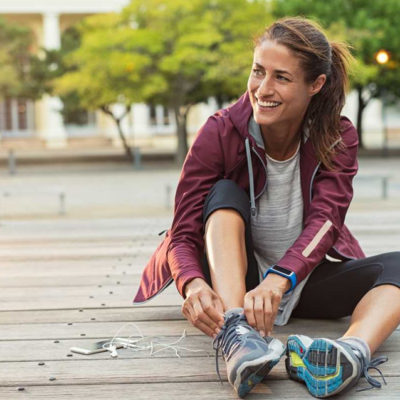
Adults With Multiple Kids Engage in Significantly Less Vigorous Physical Activity
Physical activity is a crucial component of a healthy lifestyle, yet only one in three adults in the United States meets the weekly recommendation for exercise. The struggle to stay fit is complicated even further for parents, who often prioritize their children's needs over their own. A new study, titled "The Association between Adult Sport, Fitness, and Recreational … [Read more...]
New Study Shows How Marathon Running Affects Different Foot Muscles
Foot muscles are generally categorized as either intrinsic or extrinsic muscles. While intrinsic muscles originate and insert within the foot, extrinsic muscles originate in the lower leg and insert into the foot via the ankle. Both muscle groups help stabilize the medial (inner) longitudinal arch of the foot. Although some studies have linked muscle swelling caused by … [Read more...]
Exercise Seems to Protect Against Major Brain Hemorrhage
Regular physical activity and exercise may reduce bleeding in individuals with intracerebral hemorrhage, a University of Gothenburg study shows. The researchers emphasize the importance of physical activity to protect the brain. The study, published in the journal Stroke and Vascular Neurology, analyzed data on 686 people treated for intracerebral hemorrhage at Sahlgrenska … [Read more...]
Physical Activity can Help Mental Health in Pre-teen Years
Engaging in regular moderate to vigorous physical activity at age 11 was associated with better mental health between the ages of 11 and 13, the study found. Physical activity was also associated with reduced hyperactivity and behavioural problems, such as loss of temper, fighting with other children, lying, and stealing, in young people. Researchers from the Universities … [Read more...]
Study Reveals New Understanding of How Androgen Therapy Affects Breast Tissue
Transgender men who were assigned female at birth and identify today as male may take hormones called androgens to induce physical changes that help them align their physical appearance with their identified gender. Androgens such as testosterone are involved primarily in the development of male traits, although females also produce androgens. Molecular changes observed in … [Read more...]
Combining Time-Restricted Eating and HIIT Improves Health Measures in Women with Obesity
Both time-restricted eating (TRE) and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) have been shown to improve cardiometabolic health in people who are overweight and at risk of serious disease. Now a randomized, controlled trial has tested whether combining these two approaches is more effective than either of them on their own. The results, publishing in the journal Cell Metabolism … [Read more...]
Scientists Chart How Exercise Affects The Body
Exercise is well-known to help people lose weight and avoid gaining it. However, identifying the cellular mechanisms that underlie this process has proven difficult because so many cells and tissues are involved. In a new study in mice that expands researchers' understanding of how exercise and diet affect the body, MIT and Harvard Medical School researchers have mapped out … [Read more...]
Promising Treatment For Dementia
Behavioural variant frontotemporal dementia (bvFTD) is a rapidly progressing destructive disease and can occur in people as young as 35 years of age. It is characterised by behavioural disturbances and personality changes and can be highly disruptive and distressing for both patients and their families. Currently there are no treatments or cures for bvFTD and typical survival … [Read more...]
How Migraine Pain Signals are Generated, and Blocked
An international team of researchers has discovered that Schwann cells -- which are abundant in the peripheral nervous system and create a protective sheath around nerve fibers -- play an essential role in migraine pain. Their study, conducted in mice and human Schwann cells and published in Nature Communications, illustrates how pain is signaled from within Schwann cells and … [Read more...]
Overlooked Disease: Tens of Thousands of People have Problems at work
Imagine your head pounding. And when you try to move, a door slams, or curtains are drawn it gets much worse. Ideally, you would like to crawl under your blanket in a dark and quiet room. This is how it may feel for people suffering from migraine or frequent tension headaches. Untreated, a migraine attack may last for 4-72 hours, and tension headaches may potentially last … [Read more...]
Highly Responsive Immune Cells Seem to be Beneficial For The Brain
Findings by researchers from Germany support the view that hyperactive immune cells in the brain can have a protective effect in the course of neurodegenerative diseases. Experts from Deutsches Zentrum für Neurodegenerative Erkrankungen (DZNE), Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München (LMU) and LMU Klinikum München report on this in the scientific magazine The EMBO Journal. The … [Read more...]
New Method for Stimulating Signaling to Improve Metabolic Health and Possibly Treat Obesity
Following up on a 2018 study that identified an epigenetic modifier known as histone deacetylase 11 (HDAC11) as a potential therapeutic target for treating obesity and diabetes, researchers from the University of Colorado School of Medicine have published new research that finds HDAC11 regulates G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) called beta-adrenergic receptors … [Read more...]
Overactive Bladder and Urinary Incontinence Worsen with Age
If you're feeling more sudden urges to run to the bathroom as you age, you're not alone. A new study suggests postmenopausal women aged 45 to 54 years are more likely to have overactive bladder (OAB) syndrome. Additionally, obesity and multiple births put a woman at greater risk for stress urinary incontinence (SUI). Study results are published online today in Menopause, the … [Read more...]
‘Broken heart’ syndrome is on the rise in women
The study, published in the Journal of the American Heart Association (JAHA), suggests middle-aged and older women are being diagnosed with broken heart syndrome more frequently -- up to 10 times more often -- than younger women or men of any age. The research also suggests that the rare condition has become more common, and the incidence has been rising steadily since well … [Read more...]
Higher fasting ‘hunger hormone’ levels from healthy diet may improve heart health and metabolism
Fasting levels of the "hunger hormone" ghrelin rebound after weight loss and can help reduce belly fat and improve the body's sensitivity to insulin, according to a study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. Ghrelin is a stomach-derived hormone that stimulates appetite. Ghrelin levels rise during overnight fasting when a … [Read more...]
Antibiotic Levels Measurable in Breath
A team of engineers and biotechnologists at the University of Freiburg has for the first time shown in mammals that the concentration of antibiotics in the body can be determined using breath samples. The breath measurements also corresponded to the antibiotic concentrations in the blood. The team's biosensor -- a multiplex chip that allows simultaneous measurement of several … [Read more...]
MIND Diet Linked to Better Cognitive Performance
Aging takes a toll on the body and on the mind. For example, the tissue of aging human brains sometimes develops abnormal clumps of proteins that are the hallmark of Alzheimer's disease. How can you protect your brain from these effects? Researchers at Rush University Medical Center have found that older adults may benefit from a specific diet called the MIND diet even when … [Read more...]
Many COVID-19 Patients Produce Immune Responses Against their Body’s Tissues or Organs
A University of Birmingham-led study funded by the UK Coronavirus Immunology Consortium has found that many patients with COVID-19 produce immune responses against their body's own tissues or organs. COVID-19 has been associated with a variety of unexpected symptoms, both at the time of infection and for many months afterwards. It is not fully understand what causes these … [Read more...]
Researchers Develop New Measure of Brain Health
How old is your brain compared to your chronological age? A new measure of brain health developed by researchers at Rush University Medical Center may offer a novel approach to identifying individuals at risk of memory and thinking problems, according to research results published in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association on June 1. Dubbed … [Read more...]
Brain Changes Following Traumatic Brain Injury Share Similarities With Alzheimer’s Disease
Brain changes in people with Alzheimer's disease and in those with mild traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) have significant similarities, a new USC study shows, suggesting new ways to identify patients at high risk for Alzheimer's. The findings appear this week in GeroScience. TBIs, which affect over 1.7 million Americans every year, are often followed by changes in brain … [Read more...]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 96
- Next Page »