"Inflammation of brain neurons is usually considered to be a bad thing, since it can lead to neurological problems such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease," said study leader Jelena Radulovic, M.D., Ph.D., professor in the Dominick P. Purpura Department of Neuroscience, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, and the Sylvia and Robert S. Olnick Chair in … [Read more...]
Asthma & Allergies News

Gut Bacteria Important For Overcoming Milk Allergy
Many children have allergic reactions to cow's milk, specifically to certain milk proteins. Although most grow out of it, for some it becomes a life-long challenge to avoid all foods that include milk, especially when the allergic reactions are severe and include anaphylactic shock. Researchers have found that milk allergy is improved by oral immunotherapy, a treatment in … [Read more...]
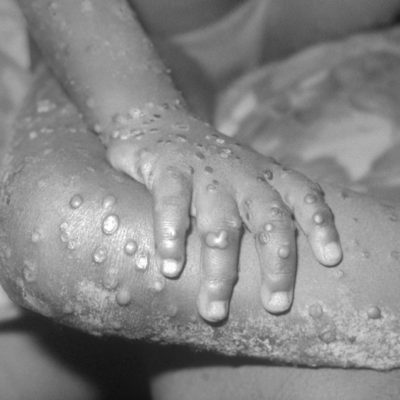
NIH Experts Review Monkeypox Challenges
Anthony S. Fauci, M.D., director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), and H. Clifford Lane, M.D., NIAID deputy director for clinical research and special projects, discuss a published case series (JP Thornhill et al.) detailing the symptoms and outcomes of 528 people with monkeypox from 16 countries in five continents. The authors note that … [Read more...]
Peanut Allergy Treatment Safest When Started For Infants Under 12 months, researchers find
Now they have evidence that the earlier pre-schoolers start this treatment, the better. This real-world study focused on infants younger than 12 months old and reveals that not only is oral immunotherapy effective against peanut allergies, it's even safer for this age group than it is for toddlers and older pre-schoolers. "This treatment is affordable, very safe and … [Read more...]
How a Leaky Gut Leads to Inflamed Lungs
Why are older adults more likely to get seriously ill or even die from pneumonia? It turns out the cause may have as much to do with the gut as it does with the lungs. That's according to new research from Rachel McMahan, PhD, assistant research professor of GI, trauma, and endocrine surgery in the University of Colorado School of Medicine, and CU School of Medicine … [Read more...]
Researchers Studying Ways to Ease Asthma Symptoms Caused by Seasonal Allergies
"Asthma has no cure and current treatments primarily focus on resolving the symptoms," said Ben Ulrich, PhD, lead author of the study. "While spending time in the high-risk asthma clinic at Riley Hospital for Children, I observed many patients had a more intermittent disease course. We went into the lab and developed models to more accurately define allergic memory and recall … [Read more...]
Fermented Soybeans Suppress Asthma-Induced Airway Inflammation
Bronchial asthma causes symptoms such as wheezing and cough due to chronic airway inflammation, but there is no fundamental treatment for it, leaving a desire for new prevention and treatment methods. Now a new study reveals that a fermented soy product called ImmuBalance suppresses airway inflammation in animal models of asthma. Researchers from the Department of … [Read more...]
Onset of Allergies including asthma and hay fever not directly causally linked to mental health traits
Allergic diseases such as asthma, atopic dermatitis and hay fever do not cause the onset of mental health conditions or vice versa, according to the findings of a new University of Bristol-led study published today (6 October) in the journal Clinical and Experimental Allergy. While previous studies have reported an observational relationship between mental health and common … [Read more...]
Scientists find a key to hepatitis C entry into cells
In a new paper published in Nature, scientists from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, describe the structure of a key protein on the surface of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) and how it interacts with its receptor found on some human cells. The findings provide new leads for developing an HCV vaccine. … [Read more...]
What Makes Us Sneeze?
"Better understanding what causes us to sneeze -- specifically how neurons behave in response to allergens and viruses -- may point to treatments capable of slowing the spread of infectious respiratory diseases via sneezes," said Qin Liu, PhD, an associate professor of anesthesiology and the study's senior investigator. The findings are published June 15 in the journal … [Read more...]
Baby’s First Stool can Help Predict Risk of Developing Allergies
It may seem like an unusual place to go looking for answers, but the contents of a baby's first diaper can reveal a lot about a newborn's future health. In a new study published today in Cell Reports Medicine, a team of University of British Columbia (UBC) researchers has shown that the composition of a baby's first poop -- a thick, dark green substance known as meconium -- … [Read more...]
Relieve Your Stress, Relieve Your Allergies
Increased allergic reactions may be tied to the corticotropin-releasing stress hormone (CRH), suggests a study published this month in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences. These findings may help clarify the mechanism by which CRH induces proliferation of mast cells (MC) -- agents involved in the development of allergies in the human nasal cavity. "In my daily … [Read more...]
Consuming omega-3 fatty acids could prevent asthma, study suggests
New research suggests that a higher dietary intake of long chain omega-3 fatty acids in childhood may reduce the risk of developing subsequent asthma, but only in children carrying a common gene variant. The study, led by Queen Mary University of London, is in collaboration with the University of Bristol and University of Southampton, UK, and Karolinska Institutet, … [Read more...]
Sweat, bleach and gym air quality: Chemical reactions make new airborne chemicals
One sweaty, huffing, exercising person emits as many chemicals from their body as up to five sedentary people, according to a new University of Colorado Boulder study. And notably, those human emissions, including amino acids from sweat or acetone from breath, chemically combine with bleach cleaners to form new airborne chemicals with unknown impacts to indoor air … [Read more...]
Warning Signs over Effectiveness of HIV ‘wonder drug’ in Sub-Saharan Africa
Dolutegravir, the current first-line treatment for HIV, may not be as effective as hoped in sub-Saharan Africa, suggests new research published on World AIDS Day. The study finds that this so-called 'wonder drug' may be less effective in patients resistant to older drugs. As HIV copies itself and replicates, it can develop errors, or 'mutations', in its genetic code (its … [Read more...]
Study Connects Diabetes, Air Pollution to Interstitial Lung Disease
People with pre-diabetes or diabetes who live in ozone-polluted areas may have an increased risk for an irreversible disease with a high mortality rate. A new study published in the Environmental Health Perspectives connects insulin resistance and repetitive ozone exposure to the development of interstitial lung disease. "Our findings are especially important today as … [Read more...]
Healthy Muscles: a Carrot on a String for Healthy Lungs
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a lung disease caused by long-term inhalation of harmful gases such as cigarette smoke. Scientists have recognized deterioration of muscle tissue, known as, as a secondary effect of damaged lungs. This frailty makes it difficult for individuals to move around and exercise, which is turn worsens the state of their lungs, causing an … [Read more...]
Scientists discover that nicotine promotes spread of lung cancer to the brain
Among people who have the most common type of lung cancer, up to 40% develop metastatic brain tumors, with an average survival time of less than six months. But why non-small-cell lung cancer so often spreads to the brain has been poorly understood. Now scientists at Wake Forest School of Medicine have found that nicotine, a non-carcinogenic chemical found in tobacco, … [Read more...]
Dementia gene raises risk of severe COVID-19
Having a faulty gene linked to dementia doubles the risk of developing severe COVID-19, according to a large-scale study. Researchers at the University of Exeter Medical School and the University of Connecticut School of Medicine analysed data from the UK Biobank, and found high risk of severe COVID-19 infection among European ancestry participants who carry two faulty … [Read more...]
Scientists shed light on action of key tuberculosis drug
A new study led by scientists at the University of Birmingham has shed fresh light on how a key front-line drug kills the tuberculosis bacterium. The research paves the way for development of new antibiotic drugs targeted at emerging strains of TB. Tuberculosis (TB) remains a global health challenge, responsible for around 1.5 million deaths each year, with particularly … [Read more...]
New understanding of asthma medicines could improve future treatment
New research has revealed new insights into common asthma aerosol treatments to aid the drug's future improvements which could benefit hundreds of millions of global sufferers. Lung diseases such as asthma are a major global health burden, with an estimated 330 million asthma sufferers worldwide. The most effective treatments are through direct inhalation of medicine to the … [Read more...]
Breastfeeding and Risks of Allergies and Asthma
Exclusive breastfeeding for 3 months was associated with a 23% lower relative risk of respiratory allergies at the age of 6 years. It was also associated with a 34% lower relative risk of asthma, but only if the children did not have a family history of asthma. Breastfeeding for 3 months, but not exclusively, was insufficient to reduce the risk of respiratory … [Read more...]
Researchers make asthma breakthrough
Researchers from Trinity College Dublin have made a breakthrough that may eventually lead to improved therapeutic options for people living with asthma. The researchers have uncovered a critical role for a protein (Caspase-11), which had previously never been implicated in the disease. They report their findings today [Wednesday 26th February 2020] in leading journal Nature … [Read more...]
Parent and sibling attitudes among top influences on teenage e-cigarette use
E-cigarette use has exploded in recent years, rising from less than 2% of high school and middle school students in 2011 to more than 27% in 2018, becoming the most commonly used tobacco product among teens, according to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC). In the wake of recent vaping-related illnesses and deaths, teenage perceptions of the products are crucial to guiding … [Read more...]
Sugar Could Be Sweet Solution To Respiratory Disease
Restriction or inhalation of common sugar could one day treat a range of respiratory diseases, according to new research led by University of Manchester biologists. The study in mice reveals how the ability of cells to use glucose helps to regulate the immune system during lung inflammation. Their research suggests that blocking sugar receptors in the lung could reduce … [Read more...]
Scientists Developing New Vaccine Strategy For Tuberculosis
For years, scientists have been trying to come up with a better way to protect people against tuberculosis, the disease caused by infection with the Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) bacteria. Texas Biomedical Research Institute Professor Jordi Torrelles, Ph.D., says new hope is on the horizon after a recent experiment performed in mice showed great promise. The study was … [Read more...]
Scientists Identify Unique Subtype Of Eczema Linked To Food Allergy
Children with atopic dermatitis develop patches of dry, itchy, scaly skin caused by allergic inflammation. Atopic dermatitis symptoms range from minor itchiness to extreme discomfort that can disrupt a child's sleep and can lead to recurrent infections in scratched, broken skin. The study, led by Donald Y.M. Leung, M.D., Ph.D., of National Jewish Health in Denver, examined … [Read more...]
Peanut Allergy Prevention Strategy Is Nutritionally Safe
Introducing peanut-containing foods during infancy as a peanut allergy prevention strategy does not compromise the duration of breastfeeding or affect children’s growth and nutritional intakes, new findings show. The work, funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, is published online on June 10 in the … [Read more...]
Pregnant women and new moms still hesitant to introduce peanut products
In January 2017 guidelines were released urging parents to begin early introduction of peanut-containing foods to reduce the risk of peanut allergy. A new study shows those who are aware of the guidelines are still hesitant to put them into place and not everyone has heard of them. The study, published in Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, the scientific journal of … [Read more...]
New Rx for allergic contact dermatitis
Research led by Nicolas Bazan, MD, PhD, Boyd Professor and Director of the Neuroscience Center of Excellence at LSU Health New Orleans School of Medicine, has found a promising new treatment for allergic contact dermatitis that offers an alternative to corticosteroids and their possible side effects. The research is published this month in Dermatology and Therapy, available … [Read more...]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 13
- Next Page »