The inefficient breakdown of fats predicts later weight gain and metabolic complications such as type 2 diabetes in women, researchers report in the journal Cell Metabolism. Low levels of hormone-stimulated lipolysis -- a biochemical process by which triglycerides are broken down into energy-rich fatty acids -- were associated with weight gain and metabolic problems 13 years … [Read more...]
Diabetes News

Why zero-calorie sweeteners can still lead to diabetes, obesity
Increased awareness of the health consequences of eating too much sugar has fueled a dramatic uptick in the consumption of zero-calorie artificial sweeteners in recent decades. However, new research finds sugar replacements can also cause health changes that are linked with diabetes and obesity, suggesting that switching from regular to diet soda may be a case of 'out of the … [Read more...]
Unexpected finding may deter disabling diabetic eye disease
A new Michigan State University study is the first to find that a particular type of lipid, or fat, thought to only exist in the skin, now lives in your eye and might play a major role in deterring the eye disease. "Our study presents an unexpected finding that the connections between cells in the retinal blood vessels contain unusual, long-chain lipids that may keep vessels … [Read more...]
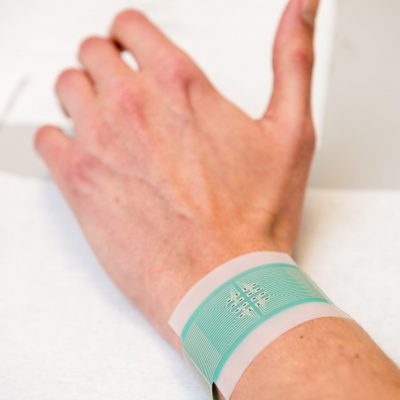
Bloodless revolution in diabetes monitoring
The patch does not pierce the skin, instead it draws glucose out from fluid between cells across hair follicles, which are individually accessed via an array of miniature sensors using a small electric current. The glucose collects in tiny reservoirs and is measured. Readings can be taken every 10 to 15 minutes over several hours. Crucially, because of the design of the … [Read more...]
Fiber-fermenting bacteria improve health of type 2 diabetes patients
The fight against type 2 diabetes may soon improve thanks to a pioneering high-fiber diet study led by a Rutgers University-New Brunswick professor. Promotion of a select group of gut bacteria by a diet high in diverse fibers led to better blood glucose control, greater weight loss and better lipid levels in people with type 2 diabetes, according to research published … [Read more...]
Arsenic-tainted drinking water may increase diabetes risk
A new study reports that chronic exposure to arsenic interferes with insulin secretion in the pancreas, which may increase the risk of diabetes. The paper, published ahead of print in the American Journal of Physiology -- Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, was chosen as an APSselect article for January. Arsenic is an element that occurs … [Read more...]
Hot flashes could be precursor to diabetes, study suggests
Hot flashes, undoubtedly the most common symptom of menopause, are not just uncomfortable and inconvenient, but numerous studies demonstrate they may increase the risk of serious health problems, including heart disease. A new study suggests that hot flashes (especially when accompanied by night sweats) also may increase the risk of developing diabetes. Results are being … [Read more...]
Mature B lymphocytes accelerate the healing of diabetic ulcers, other skin injuries
A Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) research team has found a surprising potential solution to a persistent clinical problem -- the healing of chronic wounds. In their report published in Wound Repair and Regeneration, the investigators from the MGH Vaccine and Immunotherapy Center (VIC) describe how application of mature B lymphocytes -- the immune cells best known for … [Read more...]
Understanding how gastric bypass works: Finding drug targets for obesity and diabetes
A study by a team of researchers at the Massachusetts General Hospital Center for Engineering in Medicine (MGH-CEM) and Shriners Hospital for Children has made a technological advancement toward accelerating the discovery of drug targets for obesity, type II diabetes and other metabolic diseases. The novel experimental and computational workflow involves the first use of rodent … [Read more...]
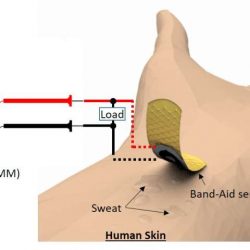
New self-powered paper patch could help diabetics measure glucose during exercise
A new paper-based sensor patch developed by researchers at Binghamton University, State University of New York could allow diabetics to effectively measure glucose levels during exercise. Today's most widespread methods for glucose self-testing involve monitoring glucose levels in blood. Conventional measurements, however, are not suitable for preventing hypoglycemia … [Read more...]
The best place to treat type 1 diabetes might be just under your skin
A group of U of T researchers have demonstrated that the space under our skin might be an optimal location to treat type 1 diabetes (T1D). The new study, led by researchers in the University of Toronto's Institute of Biomaterials & Biomedical Engineering (IBBME), involved transplanting healthy pancreatic cells under the skin to produce insulin for blood glucose … [Read more...]
Specific diabetes medications to protect bone health recommended
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) and osteoporosis often coexist in patients, but managing both conditions can be a challenge. A comprehensive review published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism highlights the most effective treatment options for treating these conditions together. Previous research has focused on the management of T2D and … [Read more...]
Number of adults with diabetes reaches 422 million worldwide, with fastest increases in low and middle income countries
Since 1980, the number of adults with diabetes worldwide has quadrupled from 108 million to 422 million, according to a new study published in The Lancet. The findings provide the most comprehensive estimates of worldwide diabetes trends to date and show that diabetes is fast becoming a major problem in low and middle income countries. "Diabetes has become a defining … [Read more...]
Sugar-free and ‘diet’ drinks no better for healthy weight than full sugar drinks
Sugar-free and "diet" drinks are often seen as the healthier option -- but researchers from Imperial College London have argued that they are no more helpful for maintaining a healthy weight than their full-sugar versions. In a commentary on current research and policy into sweetened drinks, academics from Imperial College London and two Brazilian universities … [Read more...]
New Protein Sheds Light On How Diabetes Drug Prevents Tumors
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have identified a previously unknown mechanism that helps fortify the structure and tight junctions between epithelial cells -- a basic cell type that lines various body cavities and organs throughout the body, forming a protective barrier against toxins, pathogens and inflammatory triggers. Breaches of this … [Read more...]
Insulin Resistance Reversed By Removal Of Protein
By removing the protein galectin-3 (Gal3), a team of investigators led by University of California School of Medicine researchers were able to reverse diabetic insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in mouse models of obesity and diabetes. By binding to insulin receptors on cells, Gal3 prevents insulin from attaching to the receptors resulting in cellular insulin … [Read more...]
What Causes Inflammation In Diabetes?
Inflammation is one of the main reasons why people with diabetes experience heart attacks, strokes, kidney problems and other, related complications. Now, in a surprise finding, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified a possible trigger of chronic inflammation. Too much fat in the diet promotes insulin resistance by spurring … [Read more...]
Child Obesity On An Alarming Rise!
Researchers' global estimates indicate that by 2025, some 268 million children aged 5 to 17 years may be overweight, including 91 million obese, assuming no policy interventions have proven effective at changing current trends. Timed to coincide with this year's World Obesity Day, which is observed on October 11, investigators have also released data anticipating that … [Read more...]
Depression in early pregnancy linked to gestational diabetes
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health have discovered a two-way link between depression and gestational diabetes. Women who reported feeling depressed during the first two trimesters of pregnancy were nearly twice as likely to develop gestational diabetes, according to an analysis of pregnancy records. Conversely, a separate analysis found that women who developed … [Read more...]
Extremely low birth weight babies are 4 times more likely to have abnormal blood glucose
By the time they are in their early 30s, extremely low birth weight (ELBW) babies are four times more likely to develop dysglycemia, or abnormal blood glucose, than their normal birth weight (NBW) peers. These babies who were born weighing less than 2.2 pounds are also more likely than their peer group to have higher body fat and lower lean mass in adulthood, although … [Read more...]
Children Should Eat Less Than 25 Grams Of Added Sugars Daily
Children ages 2 to 18 should eat or drink less than six teaspoons of added sugars daily, according to the scientific statement recommending a specific limit on added sugars for children, published in the American Heart Association journal Circulation. Six teaspoons of added sugars is equivalent to about 100 calories or 25 grams. "Our target recommendation is the same … [Read more...]
Does Gestational Diabetes Ups Chances Of Child Obesity?
New research shows an increased risk of childhood obesity at age 9-11 years when the mother has had gestational diabetes during pregnancy. The study is by Dr Gang Hu, Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Baton Rouge, LA, USA, and colleagues. Childhood obesity has increased dramatically in both developed and developing countries. It has been suggested that prenatal, … [Read more...]
20 Minutes Of Ultrasound Cuts High Blood Pressure
Blood pressure can significantly drop by applying 20 minutes of ultrasound to the forearm of type II diabetes patients with treatment-resistant hypertension, according to research from Japan's Tohoku University. High blood pressure is estimated to cause 7.5 million deaths worldwide and can be difficult to control in some patients with type II diabetes. Katsunori … [Read more...]
New Methods To Prevent Blindness In Diabetes
By combining data on optometry patient's eyes with advanced computational methods, Indiana University researchers have created a virtual tissue model of diabetes in the eye. The results, reported in the journal PLOS Computational Biology, show precisely how a small protein that can both damage or grow blood vessels in the eye causes vision loss and blindness in people … [Read more...]
Mannose levels may indicate diabetes risk
Even if you are not overweight, your mannose levels may indicate whether you're at risk for type 2 diabetes (T2D) or insulin resistance (IR), a Swedish study shows. Mannose, a simple sugar that occurs as a component of many natural polysaccharides, has been identified as a biomarker for diabetes, says Adil Mardinoglu, a systems biologist at KTH Royal Institute of … [Read more...]
Diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease: A new link revealed
Drugs used to treat diabetes could also be used to treat Alzheimer's disease, and vice versa, according to new research from the University of Aberdeen. This is also the first study of its kind to show that Alzheimer's disease can lead to diabetes, as opposed to diabetes occurring first as was previously thought. The study reports that Alzheimer's Disease and type 2 … [Read more...]
High blood sugar, Lower risk of brain tumor
In a surprising twist, benign brain tumors that have previously been tied to obesity and diabetes are less likely to emerge in those with high blood sugar, new research has found. The discovery could shed light on the development of meningiomas, tumors arising from the brain and spinal cord that are usually not cancerous but that can require risky surgery and affect a … [Read more...]
Mothers with diabetes more likely to also have anti-fetal brain autoantibodies
Mothers of children with autism and were diagnosed with metabolic conditions during pregnancy, particularly gestational and type 2 diabetes, were more likely to have anti-fetal brain auto-antibodies in their blood compared to healthy women of children with autism. The presence of these anti-fetal brain autoantibodies has been previously found to be specific to … [Read more...]
Role of a key hormone in type 2 diabetes: Norwegian University Study
Researchers at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) and Oxford University have found a hormone that may offer an effective treatment for type 2 diabetes. The incidence of diabetes, especially type 2 diabetes, has skyrocketed over the last few decades, according to a report from the World Health Organization. The report says that there were 108 million … [Read more...]
Single enzyme 12-LO develops of diabetes: Indiana University Study
An enzyme called 12-LO promotes the obesity-induced oxidative stress in the pancreatic cells that leads to pre-diabetes, and diabetes. 12-LO's enzymatic action is the last step in the production of certain small molecules that harm the cell, according to a team from Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. The findings will enable the development of drugs that can … [Read more...]
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- …
- 24
- Next Page »